In order to assess the potential of archaeology resources on the seabed, it is necessary to carry out exploration activities to identify and delineate the shallow and deep sea resources. To determine the area of interest and circumscribe the archeological sites, the active sonar technologies are used.
In this article we will focus on Side Scan Sonar (SSS) and Multibeam Echosounder (MBES), essential tools during underwater investigation activities. SSS and MBES can be used to detect and identifying items in port security, accident scenes, UXO tasks and they are also a commonly used tool to detect debris in energy sector.
Knowledge and competency with the side scan sonar and Multibeam Echosounder equipment are essential to interpreting the results accurately.
A Side Scan Sonar and a Multibeam Echosounder can be installed on board manned and unmanned vehicles such as Towfish, ROV, AUV, USV. They are used in marine environments, canals, rivers to identify objects, structures, potential hazardous situations, etc.
Side Scan Sonar and Multibeam Echosounder (MBES) are used widely in underwater archaeology, to provide details regarding seafloor and detecting important underwater targets, such archaeological artifacts and wrecks.
A side scan sonar is a tool that emits high-frequency conical or fan-shaped pulses through a transducer downward and map the sea floor either side of the unit. The sound waves reflects off the seafloor or objects and returns to the surface where it is detected by the transducer installed on the vehicle or ship.
Multibeam sonar systems is useful for geophysical surveying and accurate mapping of the seafloor. The acoustic waves from the transducer is emitted in the shape of a fan that spread to the downward seabed. Multibeam sonar provides a three-dimensional maps of the seafloor that is generated from different perspectives.
Side scan sonar and MBES measure water depth, seabed and water-column backscatter.
Jessica Moro
DSO
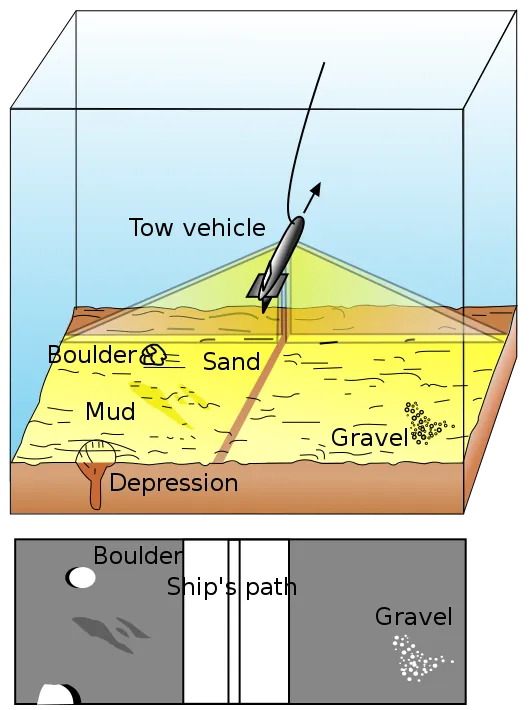
Side Scan Sonar
Used to identify objects and obtain an image of a large area of the seabed. Two transducers, one for each side, are located at the bottom of a device, such as a towfish or a remotely controlled vehicle. The reflected sonar waves are converted to an image that shows objects on the seabed. The image has a “blind strip” in the middle, which is the path of the device.
Diagram of Side Scan Sonar, from commons.wikimedia.org
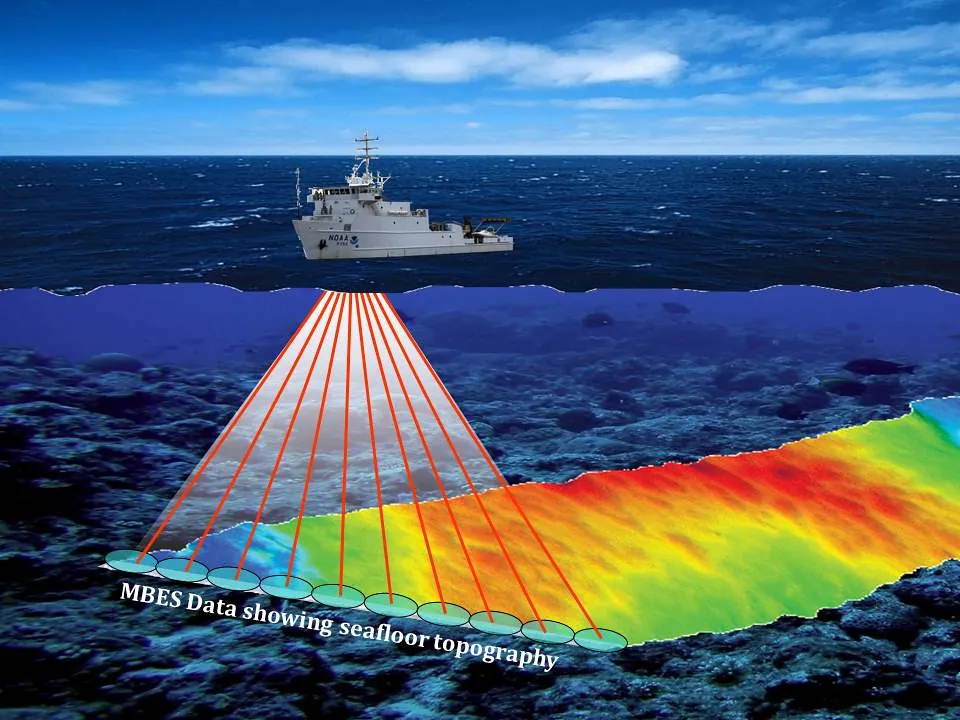
MultiBeam EchoSounder
Sonar system that emits directional acoustic beams in a fan shape; it is used to map and for bathymetric surveys of the seabed.
Artist’s conception of multibeam sonar on NOAA Ship NANCY FOSTER, Image ID: fis01334, NOAA’s Fisheries Collection, Credit: NOS/NCCOS/CCMA, from flickr.
Image
Cover: Multibeam bathymetry of Pao Pao Seamount […], NOAA Ocean Exploration & Research on flickr.

